DEFINING STUDENT SUCCESS
Students persisting to completion of their educational goals is a key gauge of student success, and therefore institutional success. Two most frequently cited statistics in connection with student success are the freshman-to-sophomore retention rate, or first-year annual return rate, and the cohort graduation rate. The freshman-to-sophomore retention rate measures the percentage of first-time, full-time students enrolled at the university the following fall semester. The cohort graduation rate is defined as the percentage of an entering class that graduates within three years with an associate’s degree, and within four, five, or six years with a baccalaureate degree. Since the annual return rate of students as they progress through a program is directly related to their degree/certificate completion, the concept of retention usually includes year-by-year retention or persistence rates as well as graduation rates. Together, these statistics represent student success.
Building strong student success is not passive but an organized and integrated effort to fulfill student expectations and institutional purpose
STUDENT SUCCESS & PERSISTENCE MANAGEMENT
Why do students leave college before completing a degree? This question is of interest not only to scholars, but also to employers, institutions, students, parents of students, and spouses. A student who leaves college before graduating paid tuition that will probably not be made up for through employment, for a person who lacks a college degree will have diminished lifetime earnings (compared to college graduates). In addition, there is a loss of tuition for the institution, a loss of a major in some department, and a loss of human capital–that is, the loss of highly trained individuals to enter the workforce or perform civic duties.
Retaining a student is fundamental to the ability of an institution to carry out its mission. A high rate of attrition (the opposite of retention) is not only a fiscal problem for schools, but a symbolic failure of an institution to achieve its purpose. Siena’ retention management effort is designed to apply intentional high touch and high-tech tools to engage students early and often to improve both the term-to-term return rates and the cohort retention rates with the primary objective to improve student success at Siena.
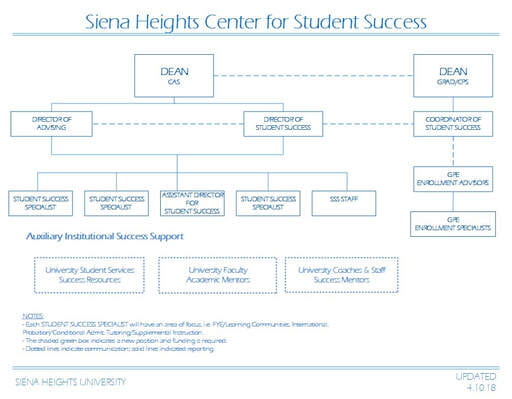
The coordinating force of Siena’s effort is the Center for Student Success (CSS), charged with bringing the institution together in its various retention activities for the purposes of student success and persistence effectiveness. The program applies a cross-divisional approach to address the tactical needs for addressing individual student needs through intrusive and holistic support from the members of Center for Student Success. Director for Student Retention (DSR) working with the members of the Student Retention Team (SRT).
In 2014, the Retention Management System (RMS) has been the primary tool to identify student retention concerns. As of 2019, the EAB tool, Navigate, is being transitioned as the primary student success student management tool for this effort Navigate is designed to assist the CSS advisor to identify potential attrition risks in the advisor’s student cohort and two provide a consolidated communication tool to coordinate identified issues and responses throughout the University.
The implementation of Navigate has created an efficient coordinating point for the implementation of retention intervention and programming.
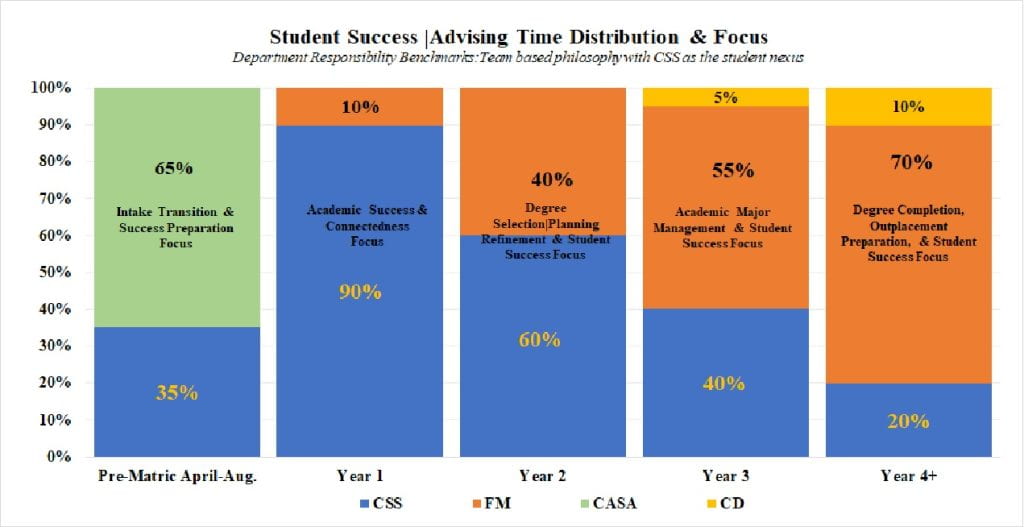
The coordination of student success and persistence activities and early intervention are the critical factors in achieving intentional student success. Often times in higher education you hear that student success is everyone job. This is true, but without direction and coordination it usually results in well intentioned efforts that lack focus and sustainable enrollment results. Intrusive student success advising and intentional persistence activities bring isolated actions together in a comprehensive institutional effort that feed a tactical and strategic enrollment plan designed to improve student and institutional success.
Siena’s student success management structure is designed to promote student success through intentional and coordinated institutional action to promote each student’s success. Critical assessment throughout the University is designed for continuous improvement for this effort. Institutional areas identified as impediments for student success will be addressed by the Student Success & Persistence Leadership Team to research options for institutional improvement. The goal is to find resolutions for systemic or operational issues that escalate attrition for the purpose to create institutional improvement.
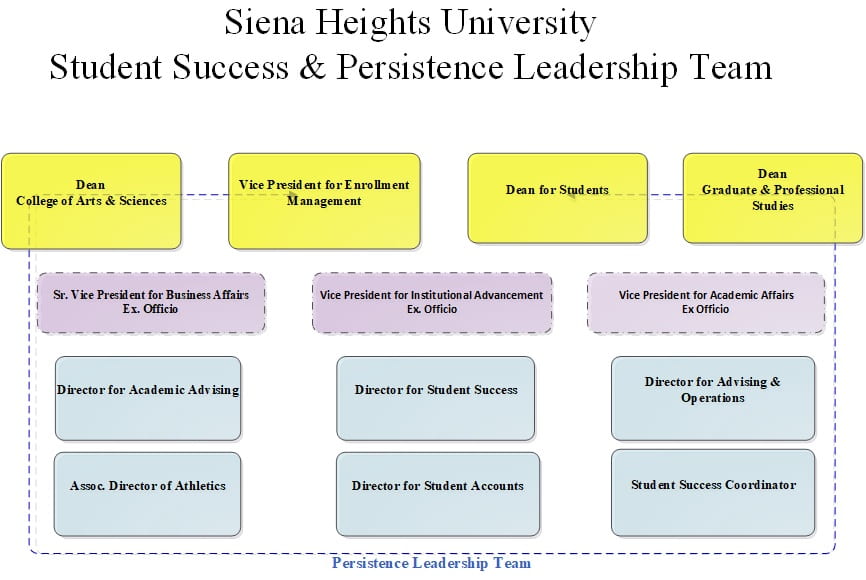
Student Success & Persistence Leadership Team
The Student Success & Persistence Leadership Team is a group of cross-divisional management staff focused on the guiding, coordinating, and assisting the efforts of the Center for Student Success and other persistence initiatives. This group uses the new EAB database tool, Navigate, along with other informational resources to identify strategic and operational directions. The leadership team is charged to integrate processes and practices across the University in order to create the best institutional environment for successful results to improve Siena’s success, persistence, and graduation rates. This group has representation from the EM, SAAS, Business and Student Life divisions.